Indoor air quality (IAQ) is a crucial consideration, as we recognize the significance of the air we breathe within buildings, be it our homes, schools, or workplaces. Devoting attention to IAQ is imperative, particularly due to the substantial amount of time we spend indoors, especially during extreme weather conditions. Poor indoor air quality can significantly impact our health, especially vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, and individuals with respiratory or cardiovascular conditions.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has identified indoor air pollution as one of the top five environmental risks to public health. The consequences of poor IAQ range from minor irritations to severe illnesses such as asthma, allergies, and even lung cancer. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that approximately 4.3 million lives are claimed annually due to exposure to indoor air pollution.
We strive to foster a harmonious relationship between nature and human well-being. By prioritizing IAQ, we contribute to creating indoor environments that support optimal health and enhance the overall quality of life for ourselves and those around us.
Common Pollutants

Indoor air quality (IAQ) is of utmost importance to like us, as we recognize the diverse sources from which indoor air pollutants can emanate. These pollutants can stem from building materials, furnishings, cleaning products, and even outdoor air pollution infiltrating our indoor spaces. Let us explore some of the most prevalent indoor air pollutants that warrant our attention:
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): These are chemicals released from various products such as paint, adhesives, and cleaning agents. VOCs can lead to irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat, as well as headaches and, in severe cases, even cancer.
Particulate Matter: These minute particles can be inhaled and pose respiratory risks, particularly for vulnerable individuals. Tobacco smoke, cooking fumes, and outdoor air pollution serve as common sources of particulate matter.
Carbon Monoxide (CO): This toxic gas arises from the combustion of fuels like gas, oil, and wood. High levels of CO exposure can result in headaches, dizziness, and even fatal consequences.
Radon: As a naturally occurring gas, radon has the potential to infiltrate buildings from the ground. Prolonged exposure to elevated radon levels can increase the risk of developing lung cancer.
Biological pollutants: This category encompasses allergens like dust mites, pet dander, and pollen, as well as mold and bacteria. Exposure to these pollutants can trigger allergies, respiratory infections, and various other health issues.
To enhance IAQ, it is essential to comprehend the sources of these pollutants and take proactive measures to minimize exposure. In the subsequent section, we will delve into effective strategies to improve indoor air quality within our homes and workplaces. By addressing these concerns, can contribute to creating healthier indoor environments that promote well-being and support a sustainable coexistence with nature.
How to Improve Indoor Air Quality
We recognize the significance of improving indoor air quality (IAQ) and its positive impact on both human health and the environment. To achieve this, several measures can be implemented, encompassing the reduction or elimination of pollutant sources, enhanced ventilation, and the utilization of air purifiers and filters. Here are some valuable tips that can contribute to enhancing IAQ:
Maintain cleanliness in your home: Regular cleaning practices assist in minimizing the accumulation of dust, dirt, and other pollutants. Opt for non-toxic cleaning products to prevent introducing additional pollutants into the air.
Control humidity levels: Excessive humidity fosters the growth of mold, which can release airborne spores. Employ a dehumidifier to maintain indoor humidity levels within the recommended range of 30% to 50%.
Promote proper ventilation: Adequate ventilation aids in diminishing the concentration of indoor air pollutants. Open windows and doors to allow fresh air circulation, utilize exhaust fans in the kitchen and bathroom, and ensure the efficient functioning of your HVAC system.
Utilize air purifiers and filters: Air purifiers equipped with HEPA filters are particularly effective in capturing small particles such as pollen, pet dander, and dust, thereby removing pollutants from the air.
Opt for low-emission products: When acquiring new furniture, building materials, or other household products, opt for options with low emissions. This choice minimizes the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the air.
Improving IAQ can yield substantial health benefits, particularly for individuals with asthma, allergies, or respiratory conditions. In the subsequent section, we will delve deeper into the specific health effects associated with poor IAQ. As Committed to promoting environmental well-being, it is imperative that we advocate for actions that improve IAQ, fostering healthier living environments for all.
Effects of Indoor Air Quality on Health
Exposure to substandard indoor air quality (IAQ) can have detrimental effects on human health, ranging from minor discomfort to severe illnesses. We understand the importance of recognizing and addressing these health concerns. Here are some of the health effects associated with indoor air pollution:
Respiratory issues: Inhalation of indoor air pollutants can irritate the eyes, nose, and throat, leading to symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions, like asthma, are particularly susceptible as indoor air pollutants can exacerbate their symptoms.
Allergic reactions: Indoor air pollutants, including dust mites, pet dander, and pollen, can trigger allergies in susceptible individuals. Symptoms may manifest as sneezing, a runny nose, and itchy eyes.
Headaches: Exposure to volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other indoor air pollutants can result in headaches and fatigue.
Cancer risk: Prolonged exposure to certain indoor air pollutants, like radon and VOCs, increases cancer risk. Experts classify these substances as known or suspected carcinogens.
Cardiovascular disease: Particulate matter and other indoor air pollutants elevate the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Vulnerable populations, including children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions, face significant risks from the health effects of poor IAQ. Taking measures to improve IAQ mitigates these health risks. The next section explores methods for testing and monitoring indoor air quality, ensuring a proactive approach to safeguarding well-being.
Testing and Monitoring Indoor Air Quality
Testing and monitoring indoor air quality is a crucial step in understanding and addressing the presence of pollutants within our living environments. We recognize the significance of maintaining a healthy indoor atmosphere. Here are some methods for testing and monitoring IAQ:
Professional indoor air quality testing: Consulting with professionals who specialize in indoor air quality testing can provide comprehensive assessments of pollutant levels. They can measure substances such as radon, VOCs, and particulate matter. Professional testing is particularly valuable if you suspect a specific pollutant is affecting your health or if you have recently relocated.
DIY testing kits: Do-it-yourself testing kits are available for certain pollutants, including radon. These kits can be easily obtained online or at hardware stores and usually involve sending a sample to a laboratory for analysis.
Carbon monoxide detectors: Installing carbon monoxide detectors in your home is crucial for detecting hazardous levels of CO gas.
Air quality monitors: Air quality monitors are devices that offer real-time measurements of particulate matter, VOCs, and other pollutants. These monitors assist in monitoring the progress of IAQ improvements over time.
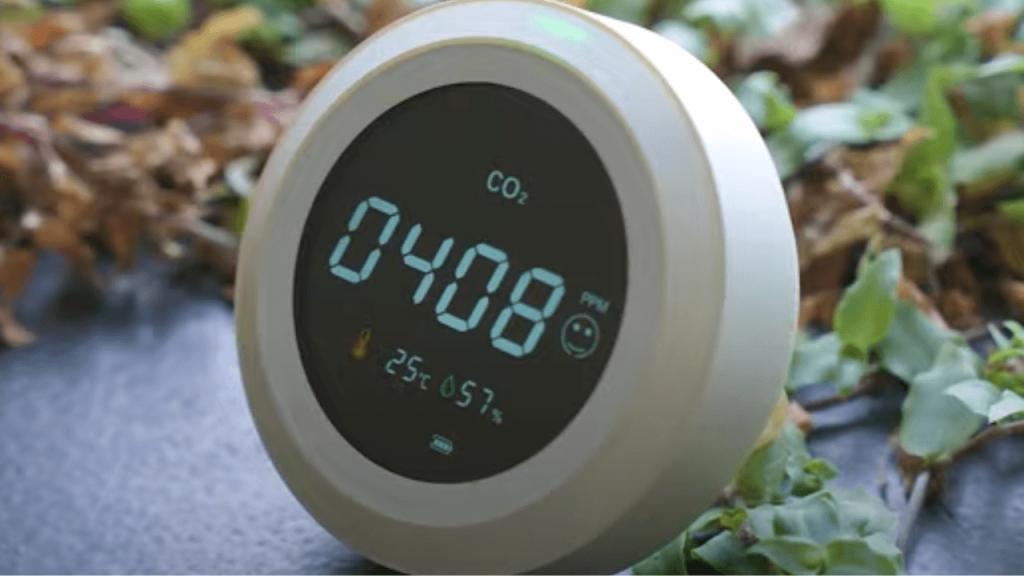

By conducting tests and maintaining ongoing monitoring of indoor air quality, you can identify potential sources of pollutants and take necessary measures to minimize exposure. This proactive approach contributes to the enhancement of your health and the well-being of your loved ones. In the final section, we will provide some concluding thoughts on the significance of indoor air quality.
Conclusion
Indoor air quality is a critical concern that directly affects our health and overall well-being. We understand the significance of maintaining a healthy indoor environment. While various sources contribute to indoor air pollution, there are numerous ways we can enhance IAQ. Through regular cleaning practices, humidity control, proper ventilation, utilization of air purifiers and filters, and opting for low-emission products, we can significantly reduce our exposure to indoor air pollutants.
Additionally, it is crucial to recognize the potential health consequences associated with poor IAQ, ranging from minor discomfort to more severe illnesses. By conducting thorough testing and ongoing monitoring of indoor air quality, we can pinpoint potential sources of pollutants and take effective measures to mitigate our exposure.
Improving indoor air quality is an ongoing journey that necessitates our continuous attention and dedication. By implementing small changes in our homes and daily routines, we can establish a healthier and safer environment for ourselves and our loved ones.