Outdoor air quality is a paramount concern and holds immense significance for the well-being of our planet. It pertains to the condition of the air we breathe in the outdoor environment and is influenced by a multitude of factors. Must comprehend the elements that affect outdoor air quality in order to undertake measures that enhance it and safeguard public health.
Among the primary threats to outdoor air quality lies air pollution. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an alarming 9 out of 10 individuals inhale air tainted with elevated levels of pollutants, contributing to approximately 7 million deaths annually. While indoor air quality is certainly crucial, the significance of outdoor air quality cannot be overstated. Given the substantial amount of time we spend outdoors and its impact on entire communities, rather than solely individuals or households, prioritizing outdoor air quality becomes paramount.
The purpose of this blog post is to provide a comprehensive overview of the Factors Affecting Outdoor Air Quality. In the subsequent sections, we will delve into the natural, human, geographic, and seasonal factors that exert an influence on outdoor air quality. Additionally, we will examine how international and national policies and regulations can play a pivotal role in the improvement of outdoor air quality. By gaining a deep understanding of these factors, can collaborate towards the enhancement of outdoor air quality, ensuring its betterment for the benefit of all.
Natural Factors and Outdoor Air Quality
Natural factors play a crucial role in shaping outdoor air quality, we must acknowledge their significant impact. Weather patterns, wind, and wildfires are among the primary natural factors that can influence the quality of the air we breathe.
Weather patterns encompass variables such as temperature, humidity, and precipitation, all of which can have consequences for outdoor air quality. High temperatures combined with low humidity, for instance, can contribute to the formation of ozone and other harmful pollutants. On the other hand, precipitation acts as a cleansing agent, aiding in the removal of pollutants from the air. Additionally, wind plays a pivotal role in the dispersion of pollutants, carrying them from one area to another and influencing air quality accordingly.
One natural factor that has a substantial impact on outdoor air quality is wildfires. These catastrophic events release a plethora of pollutants into the atmosphere, including particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The far-reaching consequences of these pollutants can have adverse effects on both human health and the environment.
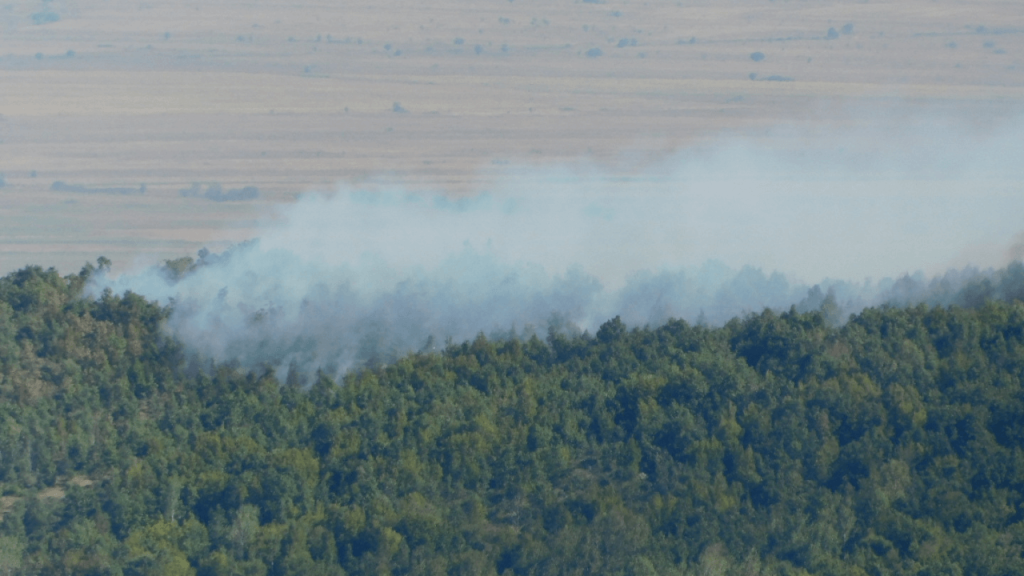

Natural factors introduce variability to outdoor air quality and influence the distribution of pollutants. While these factors lie beyond our control, must comprehend their effects on air quality and take appropriate measures to safeguard public health during periods of poor air quality stemming from natural factors such as wildfires.
Human Factors Affecting Outdoor Air Quality
Human activities have a profound influence on outdoor air pollution, and we recognize the significant role we play in addressing this issue. Several key human factors contribute to the deterioration of outdoor air quality, including transportation, industrial activity, and agriculture.
Transportation emerges as a major source of outdoor air pollution. Vehicles release a variety of pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and carbon monoxide (CO). The detrimental health effects of these pollutants are particularly pronounced in densely populated urban areas, where traffic congestion prevails.
Industrial activity stands as another prominent contributor to outdoor air pollution. Factories and power plants discharge a multitude of pollutants into the atmosphere, including sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter (PM). These pollutants have both immediate and long-term health implications, especially for individuals residing in close proximity to these pollution sources.
Agricultural practices also play a role in outdoor air pollution. Livestock production, for instance, emits substantial amounts of ammonia, which contributes to the formation of particulate matter (PM). Furthermore, the use of pesticides and fertilizers in agriculture can release pollutants into the air.
Overall, human activities exert a significant impact on outdoor air quality and public health. It is crucial to comprehend the sources of air pollution and implement appropriate measures to mitigate emissions and enhance outdoor air quality. These measures may involve promoting the use of public transportation, transitioning to clean energy sources, and adopting agricultural practices that minimize air pollution. We are committed to actively engaging in these efforts to create a healthier environment for all.
Geographic Factors Affecting Outdoor Air Quality
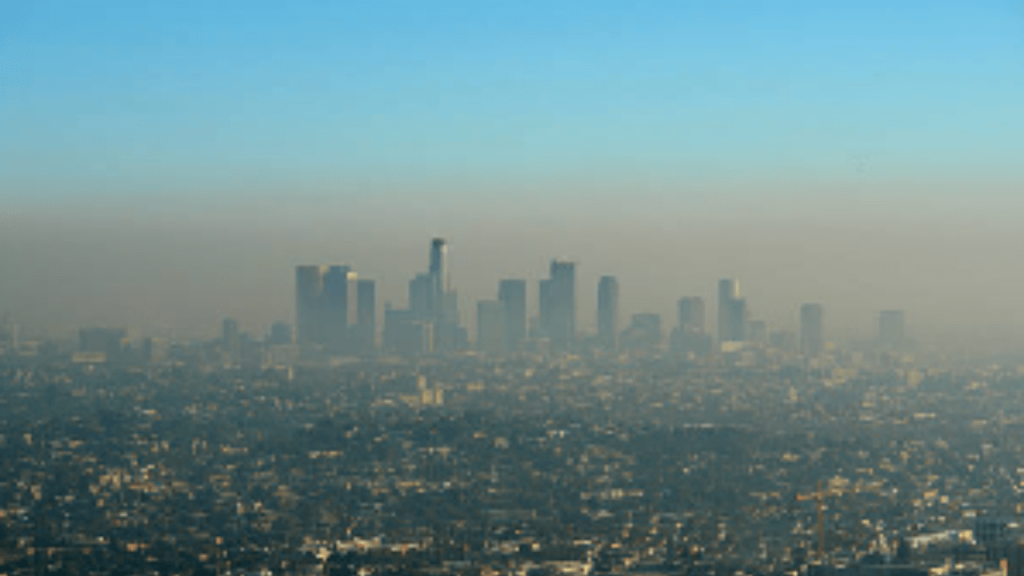

Geographical factors hold considerable importance in the context of outdoor air quality, and we recognize their significance. Several key geographical factors can influence outdoor air quality, including urbanization and topography.
Urbanization emerges as a major contributor to outdoor air pollution. Cities often exhibit high levels of traffic, industrial activity, and population density, which collectively contribute to increased air pollution. Moreover, the urban heat island effect exacerbates this issue, leading to the formation of ozone and other pollutants, particularly during hot summer months.
Topography also plays a significant role in outdoor air quality. Mountainous regions, for instance, can experience temperature inversions, where cooler air gets trapped beneath a layer of warmer air, resulting in the accumulation of pollutants. Coastal regions, on the other hand, may encounter air pollution stemming from shipping and industrial activities near ports.
In summary, geographical factors exert a substantial influence on outdoor air quality and public health. It is vital to comprehend the unique challenges faced by different regions in terms of air quality and implement appropriate measures to reduce emissions and enhance outdoor air quality. These measures may involve promoting the incorporation of green infrastructure in urban areas, monitoring air quality in vulnerable regions, and implementing regulations to control emissions from industries operating in coastal areas. We are committed to actively engaging in these efforts to create healthier environments for all.
Seasonal Factors Affecting Outdoor Air Quality
Seasonal factors have a notable influence on outdoor air quality, and we recognize their importance. Various seasonal factors can affect outdoor air quality, including temperature, precipitation, and seasonal activities.
Temperature plays a crucial role in shaping outdoor air quality by influencing the formation of pollutants such as ozone and particulate matter. During the summer months, high temperatures coupled with low humidity can result in elevated levels of ozone and other pollutants. Conversely, in winter, temperature inversions can trap pollutants close to the ground, leading to poor air quality in certain regions.
Precipitation also impacts outdoor air quality. Rainfall aids in purging pollutants from the air, while snow reflects sunlight and reduces ozone formation. However, heavy rainfall can wash pollutants into water bodies, resulting in water pollution.
Seasonal activities, including agricultural practices, can also affect outdoor air quality. For instance, the use of fertilizers and pesticides during the spring and summer months can contribute to the formation of particulate matter and other pollutants.
In summary, seasonal factors wield a significant influence on outdoor air quality and public health. It is essential to comprehend the distinct air quality challenges presented by different seasons and implement appropriate measures to diminish emissions and enhance outdoor air quality. This can encompass initiatives such as issuing air quality alerts during periods of poor air quality, adjusting agricultural practices to minimize air pollution during peak seasons, and promoting the use of public transportation during periods of high traffic. We are committed to actively engaging in these efforts to foster healthier environments for all.
Climate Change as a Factor affecting outdoor air quality
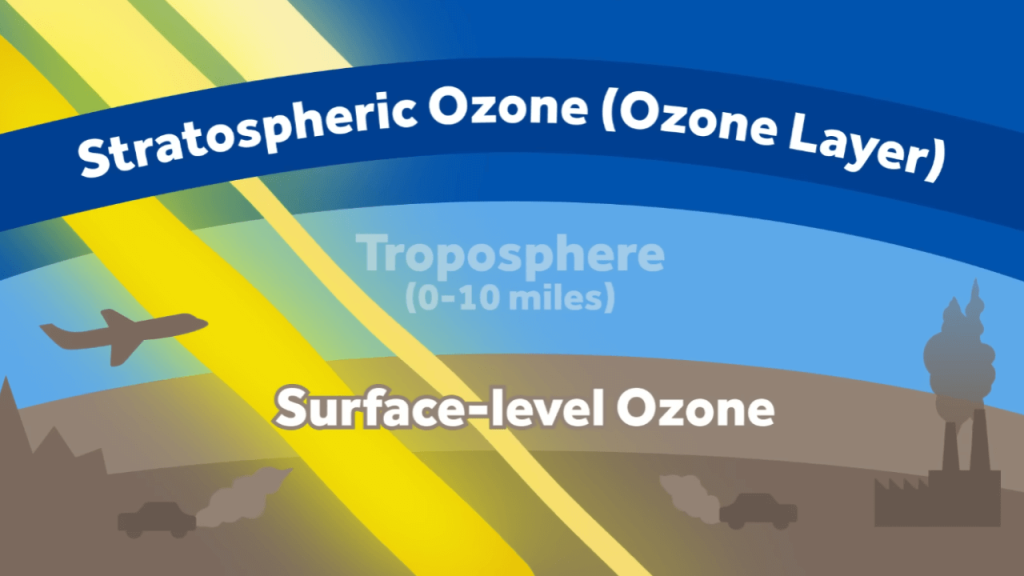
Climate change poses a critical challenge that significantly impacts outdoor air quality, and we recognize its profound implications. One of its notable impacts is the escalation in frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as heatwaves and wildfires, which release substantial amounts of air pollutants into the atmosphere. Climate change manifests in various ways, influencing outdoor air quality on a global scale.
The rising temperatures associated with climate change contribute to the increased formation of ground-level ozone, a prominent pollutant with detrimental health effects, particularly for individuals with respiratory conditions. Moreover, warmer temperatures can foster stagnant air conditions, trapping pollutants near the Earth’s surface and leading to degraded air quality.
Furthermore, climate change can influence the chemistry of the atmosphere, causing shifts in the types and quantities of pollutants present. For instance, heightened levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can alter the chemical composition of plants, affecting the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere. VOCs can react with other pollutants, contributing to the formation of harmful ozone and particulate matter.
In summary, climate change represents a significant factor that affects outdoor air quality, with its impacts poised to intensify in the years to come. It is imperative to take decisive action to address climate change by curbing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to clean energy sources. Such measures are necessary to mitigate the impacts on outdoor air quality and safeguard public health. We are committed to actively engaging in these efforts to create a healthier and sustainable environment for all.
Conclusion
Outdoor air quality is influenced by various factors, and we recognize the importance of addressing them. These factors include human activities, natural sources, geographic location, seasonal variations, and climate change. While some factors are beyond our control, such as natural sources like dust and wildfires, many others are influenced by human actions and can be mitigated through policy measures and individual initiatives.
It is crucial to acknowledge that poor outdoor air quality has significant consequences for public health, contributing to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, as well as impacting the environment. To enhance outdoor air quality and mitigate the adverse effects on public health and the environment, action must be taken at multiple levels, encompassing individuals, communities, and governments.
At the individual level, making choices such as reducing car usage, promoting active transportation, and utilizing energy-efficient appliances can all contribute to emissions reduction and the improvement of outdoor air quality. Community-level actions, such as implementing green infrastructure and advocating for sustainable land use practices, can also yield substantial improvements in outdoor air quality.
On the government front, policy measures play a vital role. These include regulating industrial emissions, promoting clean energy sources, and supporting public transportation initiatives. Furthermore, investing in research and monitoring programs to better understand the factors influencing outdoor air quality and their impacts on public health and the environment is of utmost importance.
In conclusion, enhancing outdoor air quality necessitates a collaborative effort and a commitment to emissions reduction and sustainable practices at all levels. By addressing the factors influencing outdoor air quality, we can safeguard public health, protect the environment, and foster a healthier and more sustainable future for all.

