Clean air is of utmost importance for a flourishing and thriving ecosystem. I understand the crucial role that outdoor air quality plays in maintaining the health and vitality of trees, plants, and all living organisms. It is disheartening to witness the escalating concern regarding outdoor air quality in various parts of the world.
Outdoor air quality encompasses the assessment of air quality in open spaces such as parks, streets, and public areas. The air we inhale is laden with pollutants that can have detrimental effects on our well-being, the environment, and the economy. Notably, air pollution stands as a primary catalyst for respiratory and cardiovascular ailments, inflicting harm upon both humans and wildlife, as well as impacting plant life adversely.
Regrettably, a significant number of individuals remain oblivious to the hazards posed by subpar outdoor air quality or are unaware of the measures required to safeguard themselves and their communities. Thus, it becomes imperative to raise awareness about this critical issue and take decisive actions to enhance outdoor air quality.
According to the World Health Organization, air pollution is responsible for an alarming seven million premature deaths worldwide annually. Apart from its devastating impact on human lives, poor outdoor air quality also carries economic repercussions, including escalated healthcare expenses, diminished productivity, and harm to structures and infrastructures.
This blog post aims to shed light on the factors contributing to outdoor air quality, elucidate the health ramifications of inadequate air quality, propose methods for monitoring air quality, outline steps to improve air quality and showcase successful endeavors undertaken to address this pressing concern.
Factors affecting outdoor air quality
Natural factors:
Weather patterns: Weather patterns play a vital role in shaping the outdoor air quality landscape from an arborist’s perspective. Temperature inversions, for instance, can act as barriers, trapping pollutants near the ground and impeding their dispersion. This phenomenon can significantly impact the health and vitality of trees and plants, as they become exposed to concentrated levels of harmful substances.
Wildfires: The occurrence of wildfires poses a considerable threat to outdoor air quality. These devastating events release substantial amounts of pollutants into the atmosphere, including particulate matter and carbon monoxide. The repercussions of wildfire smoke can be severe, leading to respiratory distress and hindering the growth and development of vegetation.
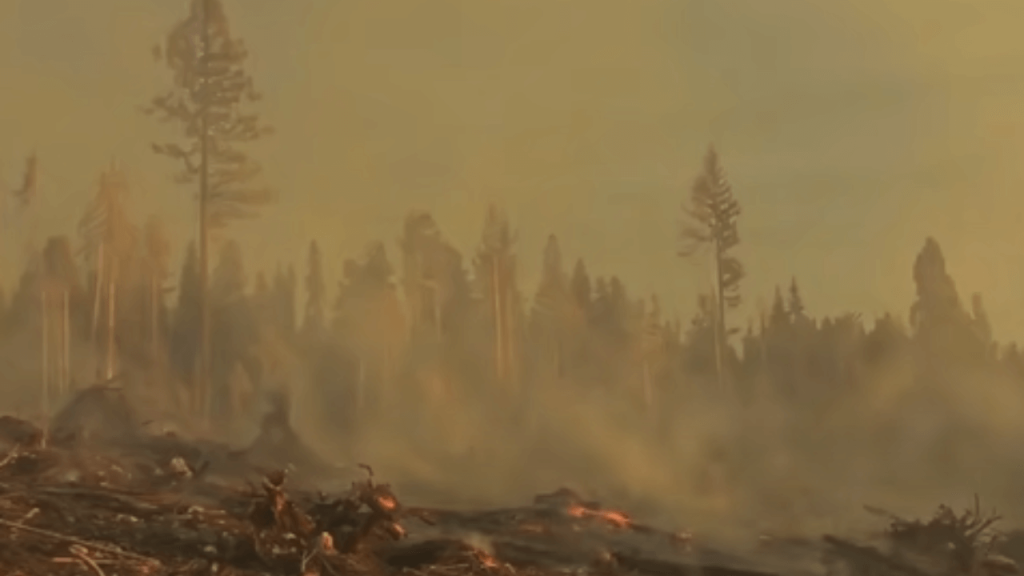

Human-made factors:
Transportation: One cannot overlook the significant contribution of transportation to air pollution, particularly in urban areas. Vehicles such as cars, trucks, and other modes of transportation emit pollutants like nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, and carbon monoxide. These emissions can have detrimental effects on the health of trees and plants, impeding their photosynthetic capabilities and overall well-being.
Industry: Industrial activities encompassing manufacturing, power generation, and construction significantly impact outdoor air quality. Smokestack emissions and chemical reactions during industrial processes are primary sources of air pollution. For arborists, the consequences of industrial emissions can manifest in various forms, including leaf damage, stunted growth, and reduced overall plant vigor.
Agriculture: From an arborist’s standpoint, it is crucial to recognize the role of agricultural practices in contributing to air pollution. Livestock farming and crop burning, for instance, release pollutants that affect the atmosphere. Methane emissions from livestock farming, which contribute to climate change, pose specific concerns for arborists due to their long-term impact on the environment and plant life.
Other factors that can influence outdoor air quality encompass natural disasters like volcanic eruptions and dust storms. These events release additional pollutants into the air, further impacting the health of trees and plants. Additionally, indoor sources of pollution, such as tobacco smoke and cooking fumes, can also indirectly affect outdoor air quality by introducing pollutants that can be carried outside.
To safeguard public health and enhance outdoor air quality, it is essential to address all these factors comprehensively. We play a crucial role in advocating for sustainable practices, promoting the preservation of green spaces, and raising awareness about the importance of clean air for the well-being of trees, plants, and the environment as a whole.
Health impacts of poor outdoor air quality
Poor outdoor air quality poses significant risks to human health, I am keenly aware of the impact it can have on individuals. Exposure to air pollution has been extensively linked to a wide range of respiratory and cardiovascular problems, as well as various other health issues. Let’s delve into some specific examples:
Respiratory problems:
Asthma: Air pollution acts as a trigger for asthma attacks and can intensify asthma symptoms, making it particularly challenging for those affected.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): Individuals with COPD, which encompasses chronic bronchitis and emphysema, face worsened symptoms when exposed to air pollution.
Lung cancer: Long-term exposure to air pollution has been associated with an increased risk of developing lung cancer, underscoring the critical need for clean air.
Cardiovascular problems:
Heart disease: Exposure to air pollution can elevate the risk of heart disease by inducing inflammation and oxidative stress, compromising the cardiovascular system.
Stroke: Scientific studies have found a correlation between air pollution and an increased risk of stroke, further emphasizing the detrimental impact of polluted air on human health.
High blood pressure: Prolonged exposure to air pollution has been linked to high blood pressure, which acts as a risk factor for both heart disease and stroke.
Other health issues:
Pregnancy complications: Air pollution poses significant risks to pregnant individuals, contributing to a range of complications including preterm birth and low birth weight.
Cognitive impairment: Research suggests a potential association between air pollution and cognitive decline and dementia in older adults, indicating the broad impact of poor air quality on overall well-being.
These examples provide a glimpse into the multitude of health impacts stemming from poor outdoor air quality. It is essential to acknowledge that the effects of air pollution can vary based on individual factors such as age, health status, and genetics. Nonetheless, the overarching message is clear: improving outdoor air quality yields substantial benefits for public health. We advocate for clean air not only for the well-being of trees and plants but also for the betterment of human lives and communities.
Methods for monitoring outdoor air quality
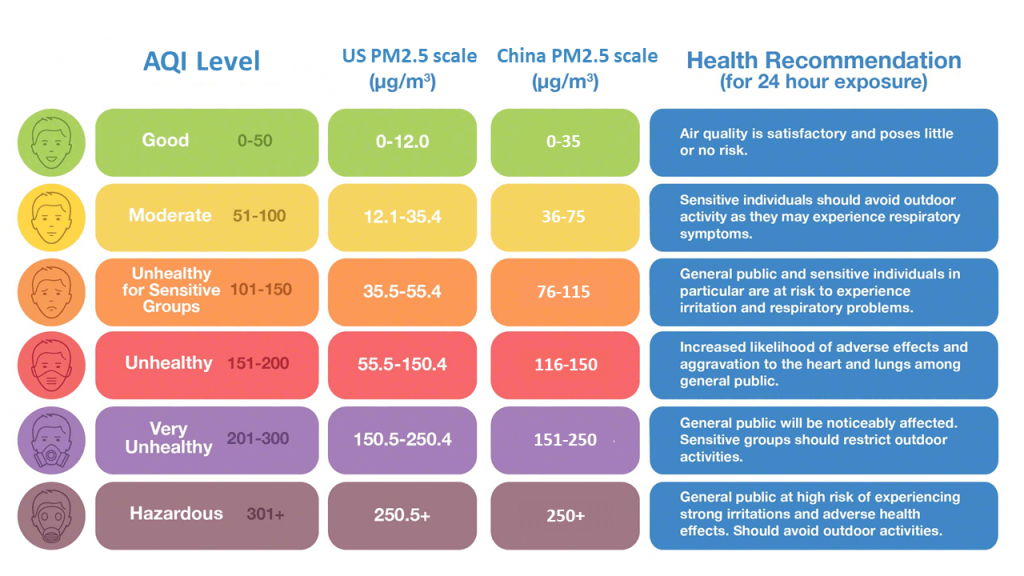
Monitoring outdoor air quality holds utmost importance for arborists as it enables us to comprehend the sources of air pollution and evaluate potential health impacts. Various methods are employed for monitoring outdoor air quality:
Government agencies:
National and local governments often establish dedicated agencies to monitor air quality. In the United States, for instance, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) operates a network of air quality monitoring stations. In the European Union, the European Environment Agency (EEA) coordinates air quality monitoring efforts across member states.
These agencies utilize diverse methodologies to monitor air quality, encompassing data collection from stationary air quality monitoring stations, mobile monitoring units, and satellite imagery.
Private organizations:
Private companies also contribute to monitoring outdoor air quality. Some companies offer affordable air quality monitors that individuals can utilize to assess air quality in their respective communities. These monitors can be deployed in residences, schools, and other locations to gather local air quality data.
Citizen science initiatives:
Citizen science initiatives involve active participation from the public in data collection and analysis. Regarding outdoor air quality, citizen science initiatives engage community members in using low-cost air quality monitors to collect local air quality data. This valuable information can then be shared with government agencies and other organizations to facilitate efforts aimed at improving air quality.
In summary, monitoring outdoor air quality constitutes a crucial step in comprehending the sources of air pollution and evaluating potential health impacts. Through a combination of government monitoring, private sector initiatives, and citizen science efforts, we enhance our understanding of air quality and take decisive measures to safeguard public health. We recognize the significance of monitoring air quality to protect the well-being of trees, plants, and the overall environment.
Ways to improve outdoor air quality
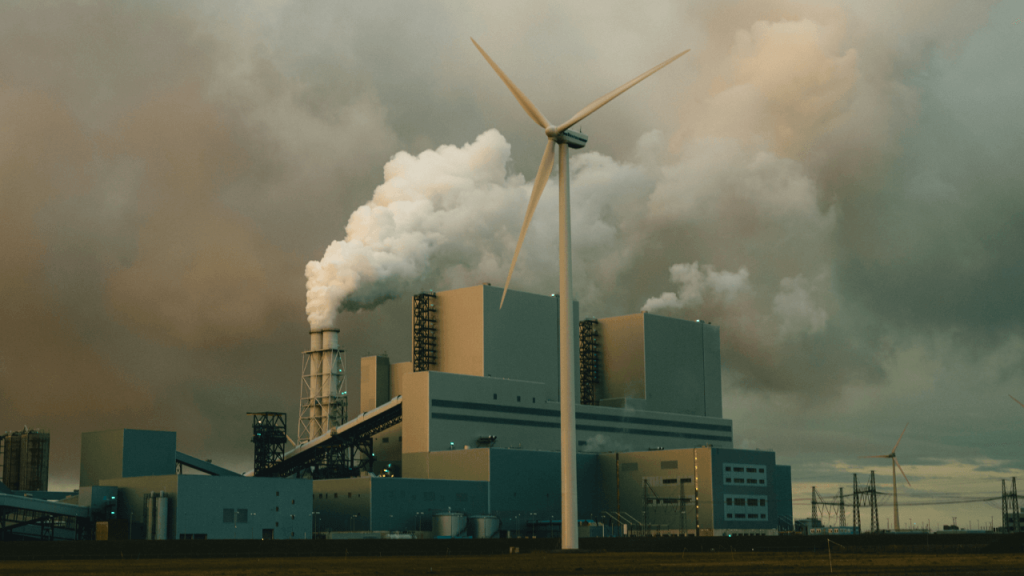

Improving outdoor air quality is a collective responsibility that involves concerted efforts from individuals, governments, and businesses. We understand the significance of proactive measures to enhance air quality. Here are some ways we can collaborate to achieve this goal:
Individual actions:
Reduce car use: Cars contribute significantly to air pollution. By opting for alternative modes of transportation such as walking, biking, or using public transit, we can effectively reduce emissions and improve air quality in our communities.
Use energy-efficient appliances: Embracing energy-efficient appliances and light bulbs minimizes energy consumption, which, in turn, reduces air pollution stemming from power plants.
Properly dispose of hazardous waste: To prevent the contamination of air and water, it is crucial to ensure the proper disposal of hazardous waste items like batteries, electronics, and chemicals.
Government actions:
Implement regulations on industry and transportation: Governments can establish regulations to limit air pollution from industrial activities and transportation. Vehicle emission standards, for instance, can significantly reduce pollution from cars and trucks.
Promote renewable energy: Governments can actively promote the adoption of renewable energy sources like wind and solar power, thereby reducing air pollution associated with fossil fuel power plants.
Invest in public transportation: By investing in efficient and accessible public transportation systems, governments can encourage people to rely less on personal vehicles, thus mitigating air pollution.
Business actions:
Implement sustainable practices: Businesses can embrace sustainable practices such as waste reduction, energy conservation, and the utilization of renewable energy sources. These measures contribute to reducing environmental impacts, including air pollution.
Provide alternatives to driving: Businesses can foster alternatives to driving, such as telecommuting, carpooling, and supporting the use of public transportation. Encouraging employees to reduce reliance on cars aids in decreasing air pollution.
Conclusion
Outdoor air quality is a critical concern from an arborist’s perspective as it directly impacts the health of trees, plants, and the overall environment. It is imperative that we join forces to enhance air quality and safeguard public health.
Various sources contribute to outdoor air pollution, including transportation, industrial activities, and natural occurrences such as wildfires and dust storms. These sources emit pollutants that pose risks to both human well-being and the environment.
To tackle this issue, multiple methods for monitoring outdoor air quality are available, encompassing government monitoring, private sector initiatives, and citizen science efforts. These monitoring approaches yield valuable data that enhance our understanding of air pollution and aid in the implementation of effective measures for its reduction.
Improving outdoor air quality necessitates collaborative action from individuals, governments, and businesses. There exist numerous approaches to combat air pollution, including utilizing public transportation, promoting renewable energy sources, and incorporating sustainable practices into our daily lives.
It is vital to acknowledge that the responsibility for enhancing outdoor air quality lies not solely with individuals, but with our collective efforts. By collaborating harmoniously, we can forge a path towards a cleaner and healthier environment, benefiting ourselves and future generations.
In conclusion, addressing outdoor air quality is paramount for the well-being of trees, plants, and the entire ecosystem. By actively working together to reduce air pollution, we safeguard our health and pave the way for a sustainable future. We advocate tirelessly for the protection of the environment and its vital resources, including clean and pristine air.

